Documentation of the CoAx Dataset
Lagamtzis, Dimitrios; Schmidt, Fabian; Seyler, Jan; and Dang, Thao
accepted at ICAART 2022 - published by SCITEPRESS
pdf
dataset
doi
Sequential Task Descriptions
Task 1: Valve Terminal Plug & Play
In this task a human agent is setting up a valve terminal with a valve. This involves actions like screwing the valve into the valve terminal and also grabbing and installing a hose. The screws are already placed in their position for simplicity reasons. This task is intended to show a typical assembly as it might occur in a collaborative industrial workspace.
Task 2: Valve Assembly
In this particular task, a valve is assembled from its individual parts. The screws belong to the actual objects of the scene and are located in a designated box. Two screws are used to assemble the main modules of the valve. The last step in the assembly is the attachment of the membrane in its designated place, likewise, stored in a box in the scene.
Task 3: Collaborative Soldering
The final task explicitly shows a collaboration between the human actor and the robot in the workspace. The robot assists the human in a soldering task by acting as a third arm. Once the robot recognizes the human's intention to solder, it reaches the soldering board, holding it for the human and aligning it so that the human can solder a capacitor onto it. This task involves the human waiting for the robot in order to continue.
Object annotation
| ID | Object | Human Readable |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | screwdriver | Screwdriver |
| 1 | hose | Hose |
| 2 | valve | Valve |
| 3 | valve_terminal | Valve terminal |
| 4 | box_w_screws | Box with screws |
| 5 | box_w_membrane | Box with membrane |
| 6 | soldering_station | Soldering station |
| 7 | soldering_iron | Soldering iron |
| 8 | soldering_tin | Soldering tin |
| 9 | soldering_board | Soldering board |
| 10 | capacitor | Capacitor |
| 11 | robot | Robot |
| 12 | human | Human |
| 13 | RightHand | Right hand |
| 14 | eef_robot | Robot's end effector |
| 15 | robot_base | Robot's base |
Action annotation - sequential order
| Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 |
|---|---|---|
| approach | approach | approach |
| grab valve | grab valve | grab capacitor |
| plug valve | join valve components | wait for robot |
| grab screwdriver | grab screws | plug capacitor |
| screw valve | plug screws | wait for robot |
| release screwdriver | grab screws | grab soldering tin |
| grab hose | plug screws | grab soldering iron |
| plug hose | grab screwdriver | solder capacitor |
| retreat | screw valve | release soldering iron |
| release screwdriver | release soldering tin | |
| place valve | retreat | |
| grab membrane | ||
| place membrane | ||
| retreat |
Action annotation - encoded with object relations
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| valve | capacitor | screwdriver | screws | membrane | soldering tin | soldering iron | hose | ||
| 0 | approach | ||||||||
| 1 | grab | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 2 | plug | X | X | X | X | ||||
| 3 | join | X | |||||||
| 4 | wait for robot | ||||||||
| 5 | screw | X | |||||||
| 6 | release | X | X | X | |||||
| 7 | solder | X | |||||||
| 8 | place | X | X | ||||||
| 9 | retreat |
Encoded Action Object Example:
Example of the approaching action from frame 0 to 50:
[0,null] refers to action with ID == 0(approach) and no action object (null)
{"right_hand": [0, [0,null], 50]}
Example of grabbing capacitor action from frame 75 to 100:
{"right_hand": [75, [1,1], 100]}
Derived Data
Information in 2D and 3D for each frame of each recorded sequence for every object in the scene. The 2D bounding boxes are given in pixel coordinates. The 3D bounding box units are in meters; in the robot’s coordinate system. To capture the dataset, an Intel RealSense Depth Camera D435 was used, capturing images at 15 fps with a resolution of 640 px × 480 px.
{
"bounding_box": {
"x0": -0.6319517876324395,
"x1": -0.4992021971049271,
"y0": -0.363614762245568,
"y1": -0.33810236065083654,
"z0": -0.29955900722097994,
"z1": -0.2845506851112529
},
"certainty": 1.0,
"class_index": 0,
"class_name": "screwdriver",
"colour": [0.18431, 0.3098, 0.3098],
"instance_name": "screwdriver_0",
"past_bounding_box": {
"x0": -0.6286039463676328,
"x1": -0.5072747525732543,
"y0": -0.3633770115164791,
"y1": -0.3387509672664858,
"z0": -0.29565532742319667,
"z1": -0.2746970149582395
}
}
As referenced in our paper, we adapted the format of our dataset from [1].
Dataset samples
How you can load the dataset and work with the derived data. Short intro and hands-on by showing a code snippet using a jupyter notebook. Utility functions are encapsulated in a util.py, that can be located in the src directory of our dataset’s GitHub-Repository.
Here we give a short preview of the repository and its functionalities:
Get images and depth images for selected identifier sequence
❗it is important to set the flag flags=-1, when reading in the depth images with cv2.imread(file,flags=-1)
images = [cv2.imread(file) for file in sorted(glob.glob(img_path+identifier+"*.png"))]
depth_images = [cv2.imread(file,flags=-1) for file in sorted(glob.glob(dpth_img_path+identifier+"*.png"))]
Plot rgb and depth image
frame_id = 70
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(images[frame_id], cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB ));

plt.imshow(depth_images[frame_id]);

Choose whichframe you want to investigate closer or loop over all frames
frame_id = 70
rgbxyz = coax.get_rgb_xyz_for_frame(frame=frame_id,
images=images,
depth_images=depth_images,
camParams=camParams)
Get 3D Bounding Boxes of every object for every frame
- Get processed dataframes for every frame
- Plot Pointcloud with 3D Object Bounding Boxes and center points
dfs_3d, obj_dfs_3d = coax.get_3d_processed_dfs_per_frame(
derived_data_path=derived_data_path,
identifier=identifier)
%matplotlib inline
coax.plot_rgbxyz_with_bounding_boxes(frame=frame_id,
rgbxyz=rgbxyz,
obj_dfs=obj_dfs_3d,
save=False)
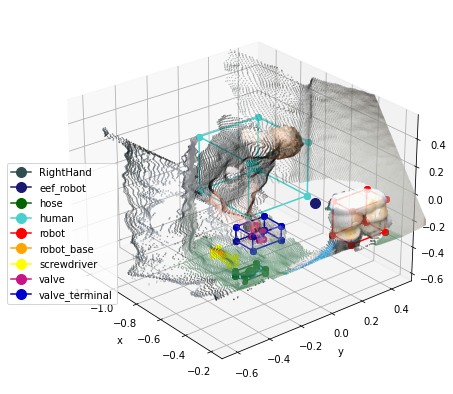
Get 2D Bounding Boxes of every object for every frame
- Get processed dataframes for every frame
- Plot Pixel-Image with 2D Object Bounding Boxes and center points
dfs_2d, obj_dfs_2d = coax.get_2d_processed_dfs_per_frame(
derived_data_path=derived_data_path,
identifier=identifier)
%matplotlib inline
coax.plot_rgb_with_bounding_boxes(frame=frame_id,
images=images,
obj_dfs=obj_dfs_2d,
save=False)
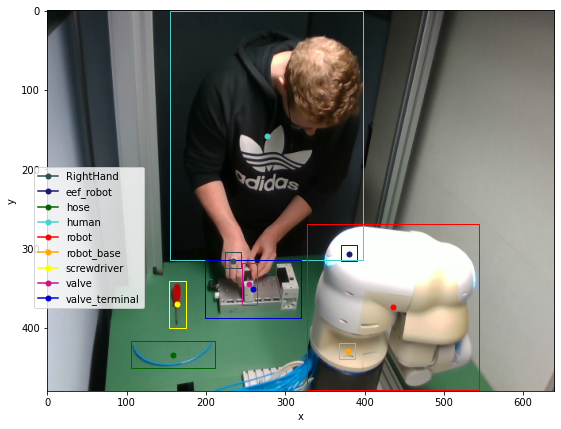
You can find further instructions on how to work with the dataset on our GitHub-Repository.